cobb test scoliosis|cobb angle for scoliosis surgery : distributor The most-commonly prescribed brace for scoliosis today is the Boston brace. . web6 de nov. de 2023 · CMI - Centro Médico Integrado, Pará, comentários de clientes, mapa de localização, números de telefone, horário de trabalho BRASILLOCAIS.COM Para comerciantes
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB3 de jan. de 2024 · Av. Morvan Dias de Figueiredo, 3177, Carrefour Vila Maria, São Paulo, Brasil, 02063-000
Here is a general outline of Cobb angle ranges and what they could indicate in idiopathic scoliosis found in children and adolescents: 1 to 9-degree curve. Curves that are less than 10 degrees are not considered to represent scoliosis, but rather a minor spinal asymmetry.The most-commonly prescribed brace for scoliosis today is the Boston brace. .
In general, the following factors increase a person’s risk for a scoliosis curve to .Any sideways spinal curve of at least 10 degrees, as measured by the Cobb . The Cobb angle is a measurement of the spine that doctors use to diagnose scoliosis, monitor spinal curvature, and determine treatment options. Learn more. It is defined by a lateral curvature of the spine (Cobb angle) of at least 10 degrees in the absence of underlying congenital or neuromuscular abnormalities. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis may be.
The Cobb angle measurement has become the “gold standard” of scoliosis evaluation endorsed by Scoliosis Research Society and as such is used as the standard measurement to quantify and track the progression of scoliosis.Someone is considered to have scoliosis when the spine has a sideways curvature of at least 10 degrees, which is measured by the Cobb angle. With this measurement, doctors are able to judge the severity of the scoliosis, assess .The orthopedic “Gold Standard” for the assessment of scoliosis is the Cobb angle, which is measured by determining the most-tilted spinal bones (vertebrae) in each curve. Lines are drawn along the top of the superior tilted vertebra and .
What is the Cobb Angle? The Cobb Angle is the cornerstone in evaluating the magnitude of spinal curvature. This measurement is crucial for diagnosing scoliosis and determining the appropriate course of treatment. A scoliometer measurement is sometimes referred to as Cobb angle — the measurement your provider will use to diagnose and track scoliosis. They’re not different kinds .The Cobb Angle is used as a standard measurement to determine and track the progression of scoliosis. Dr John Cobb invented this method in 1948. [1] How to calculate Cobb angle. The main screening test for scoliosis is the Adam’s test, . This can confirm the presence of scoliosis. A doctor will then use the X-ray to calculate the Cobb angle measurement, which tells .
Your X-rays will be evaluated and any curves in your spine will be measured in degrees using the Cobb method. A curve greater than 10º is considered scoliosis, but treatment usually isn’t necessary unless/until the curve reaches 25º. . This test, called the Adams test, is a very sensitive test for scoliosis; it is therefore the most . When it comes to scoliosis, early detection is important and increases the chances of successful treatment. While there are tests and visual assessments that can be done to screen for indicators of the condition, when it .
While there are numerous systems in place for assessing scoliosis, the Scoliometer test, Cobb angle, and the Risser-Ferguson Method are the most common. These methods are effective ways to screen for the condition, classify the condition’s severity based on the degree of curvature, and determine where an adolescent is in terms of skeletal .How to calculate Cobb angle. [edit | edit source]Cobb suggested that the angle of curvature be measured by drawing lines parallel to the upper border of the upper vertebral body and the lower border of the lowest vertebra of the structural curve, then erecting perpendiculars from these lines to cross each other, the angle between these perpendiculars being the ‘angle of curvature’.In other words, a 40 degree Cobb angle is more than twice as severe as a 20 degree Cobb angle. Reducing a 60 degree scoliosis by 10 degrees represents a far greater accomplishment than reducing a 20 degree scoliosis down to 10 degrees. As the Cobb angle increases, the actual curvature of the spine becomes exponentially more severe. .During this test, known as the Adams forward bend test, the doctor may use a sociometer—a device similar to a level—to measure the degree of spinal rotation. . (Scoliosis is diagnosed when the Cobb angle is over 10 degrees.) In some cases, the doctor may also order additional imaging tests, such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan .
4 Key Takeaways. Cobb Angle’s Role in Scoliosis Assessment: The Cobb angle is the orthopedic gold standard for diagnosing and assessing scoliosis severity. Measured in degrees, it provides crucial information on how far a patient’s spine deviates from normal alignment, guiding treatment approaches. The Cobb angle is a measurement of the spine that doctors use to diagnose scoliosis, monitor spinal curvature, and determine treatment options. Learn more.By convention, scoliosis is defined as a curvature of at least 10° (as measured by the Cobb angle 1 on an anteroposterior x-ray of the spine); . Forward Bend Test. Most school-based scoliosis screening programs use the forward bend test (FBT), commonly attributed to .
driving test portion is hard
In most instances, scoliosis is obvious if severe. On examination, the Adams forward bend test (a clinical test for assessing scoliosis) may be positive where a rib hump forms on the side of the convexity. Pathology Etiology. . The Cobb angle was first described in 1948 by American orthopedic surgeon John R Cobb (1903-1967) 7.
scoliosis cobb angle 15 degrees
Cobb angle measurement is the degree of scoliosis as measured on x-ray. Any measurement greater than 10º is considered scoliosis. Scoliosis is classified as mild, moderate or severe. See our illustration which shows how Cobb angle is determined by your doctor or radiologist.
This article is the first in a commissioned series on paediatric orthopaedics. Scoliosis is a common paediatric condition with a prevalence of 0.47–5.2%. 1 It is a three-dimensional deformity with a coronal plane Cobb angle >10° and rotation evident at the apex of the curve. 2 Males and females are equally affected for small curves. However, females are seven times more likely to . if inclinometer is > 6°, the test is suggestive for scoliosis. normal neurologic exam. Imaging. Radiographs. indications. for all patients suspected of having scoliosis. confirms diagnosis. recommend view. coronal posteroanterior spinal radiographs. finding. Cobb angle (lateral curvature of spine) . If the test yields positive results, the Cobb angle is determined to guide the patient’s treatment plan. . Cobb Angle Scoliosis Measurements. The spine’s curvature becomes quantified in degrees by the Cobb angle. This aids .
driving test too hard
Scoliosis is an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine. It is most often diagnosed in childhood or early adolescence. . confirmed through a physical examination, an x-ray, spinal radiograph, CT scan or MRI. The curve is measured by the Cobb Method and is diagnosed in terms of severity by the number of degrees. . During this test, the . A Scoliosis Diagnosis. A Scoliosis diagnosis is given when an abnormal curvature is measured at 10+ degrees and includes rotation, which is what makes scoliosis a 3-dimensional condition.. Traditional treatment: even . The condition of a spine is associated with the spinal curve instead of scoliosis when the Cobb angle is less than 10 degrees. A Cobb angle in the range of 10 to 20 degrees is considered as mild scoliosis. Scoliosis severity is moderate when the Cobb angle ranges from 20 to 40 degrees. A Cobb angle greater than 40 degrees denotes severe scoliosis. Kyphoscoliosis is defined as a deviation of the normal curvature of the spine in the sagittal and coronal planes and can include a rotation of the spinal axis.[1] Adult scoliosis is defined as a lateral deviation of more than 10 degrees in the coronal plane as measured by the Cobb angle. Lateral deviations of less than 10 degrees can be attributed to postural variation. .
If idiopathic scoliosis is suspected, radiography is used to confirm the diagnosis and to quantify the degree of curvature (i.e., the Cobb angle) and the Risser sign (the stage of ossification of . Mild scoliosis: Cobb angle measurement of between 10 and 25 degrees. Moderate scoliosis: . We have also talked about screening and assessing scoliosis via observation, the Adam’s forward bend test, the Scoliometer, the scoliosis X-ray and Cobb angle, and last but not least, the Risser-Ferguson method. . If idiopathic scoliosis is suspected, radiography is used to confirm the diagnosis and to quantify the degree of curvature (ie, the Cobb angle) and the Risser sign (the stage of ossification of the iliac apophysis). 1 US organizations that advocate screening recommend the forward bend test combined with scoliometer measurement. Scoliosis is defined as a lateral spinal curvature with a Cobb angle of 10° or more. This abnormal curvature may be the result of an underlying congenital or developmental osseous or neurologic abnormality, but in most cases the cause is unknown. Imaging modalities such as radiography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging play pivotal .
The scoliosis Cobb angle is an important index of disease assessment. The classical method is used to determine the upper/lower end vertebras (UEV/LEV) on the whole spine anteroposterior X-ray film; then, draw a vertical line respectively at the upper/lower end vertebra endplate lines (UEVEL/LEVEL), and the included angle of the two vertical lines is the .Patients with severe scoliosis (Cobb angle of 40 degrees or more) may have physical pain, cosmetic defor- . Forward bend test for scoliosis screening. The patient stands and bends forward at the . Anything more than a 10-degree curve means you have scoliosis. You’ll probably need follow-up scoliometer readings to make sure it doesn’t get more severe over time. Scoliometer vs. Cobb angle. A scoliometer measurement is sometimes referred to as Cobb angle — the measurement your provider will use to diagnose and track scoliosis.
Mild scoliosis: Cobb angle measurement of between 10 and 25 degrees; Moderate scoliosis: Cobb angle measurement of between 25 and 40 degrees; Severe scoliosis: Cobb angle measurement of 40+ degrees; Very-severe scoliosis: 80+ degrees; As a progressive condition, however, where a scoliosis is at the time of diagnosis is not indicative of where .
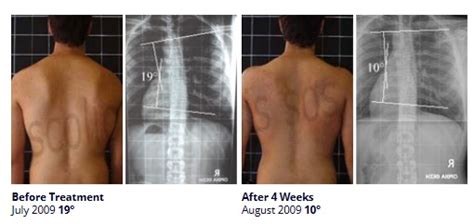
how to measure scoliosis angle
Resultado da 5 de dez. de 2023 · 查看演示. 概述. 儿-江. 在科幻的基础上披上了一层奇幻的外衣。. 世界上充斥着人工智能,它们中的大多数看起来都与人类无异. .
cobb test scoliosis|cobb angle for scoliosis surgery